Project Management Basics: Difference between revisions
Cristelags (talk | contribs) Added content |
Cristelags (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
This section reviews a few of the basic building blocks for the other sections of the toolkit. Please contribute additional project management fundamentals or other examples to the '''[[DLF Project Managers Toolkit]]'''. | |||
[[File:ProjectBasics.png|thumb|right]] | [[File:ProjectBasics.png|thumb|right]] | ||
A ''' | A '''PROJECT''' must have a defined objective (product, service, result) with a start and a finish. Projects should not be confused with ongoing work. For example, a digitization unit with regular requests for digitization is ongoing work, whereas a project would be to digitize a certain number of objects by a certain date. | ||
'''PROJECT MANAGEMENT''' is the application of knowledge, skills, tools and techniques to carry out a project. | |||
A ''' | A '''PROJECT MANAGER''' oversees the project life cycle from planning, scheduling, executing, monitoring and controlling, and closing. There should only be one project manager in a project. Important characteristics for project managers are to be knowledgeable, performance-driven, and an effective communicator. | ||
[[File:ProjectPhases.png|thumb|right]] | [[File:ProjectPhases.png|thumb|right]] | ||
''' | '''PROJECT PHASES''' include initiation, planning, implementation, and closing. | ||
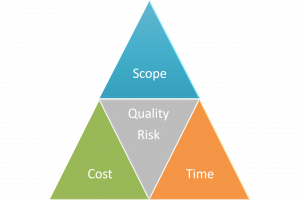
There are different factors or constraints to monitor and control in a project. Commonly known as the ''' | There are different factors or constraints to monitor and control in a project. Commonly known as the '''TRIPLE CONSTRAINT''', the scope, time, and cost are managed and adjust in a project. Quality and risk should also be considered. | ||
[[File:TripleConstraint.png|thumb|right]] | [[File:TripleConstraint.png|thumb|right]] | ||
Project Management provides a framework and best practices for projects. | Project Management provides a framework and best practices for projects. For example, the following formula can be used to estimate the time of a task. | ||
'''Three-Point Estimate''' | '''Three-Point Estimate''' | ||
| Line 29: | Line 28: | ||
Duration = (D(o) + 4D(r) + D(p)) / 6 | Duration = (D(o) + 4D(r) + D(p)) / 6 | ||
Critical to the success of any project is communication. Before beginning a project, consider the frequency (weekly, monthly, quarterly) and methods of communication (email, im, in-person; frequency of meeting). A communication plan should include the who, what, when, where, why & how. See the '''[[Project Templates]]''' of the '''[[DLF Project Managers Toolkit]] | Critical to the success of any project is communication. Before beginning a project, consider the frequency (weekly, monthly, quarterly) and methods of communication (email, im, in-person; frequency of meeting). A communication plan should include the who, what, when, where, why & how. See the '''[[Project Templates]]''' of the '''[[DLF Project Managers Toolkit]]''' for an example of a communication plan. | ||
''' for an example of a communication plan. | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
* Project Management Institute. 2018. A guide to the project management body of knowledge: (PMBOK® guide). Newtown Square, Pennsylvania, USA: Project Management Institute. | |||
* Tate, Karen, and Cynthia Snyder. 2006. The advanced project management memory jogger: a pocket guide for experienced project professionals. Salem, NH: GOAL/QPC. | |||
There are lots of great articles, presentations and grey lit out there on project management and digital libraries. We've created a Zotero Group library at https://www.zotero.org/groups/2205688/dlf_pmg? and encourage you to add more when you read something good. | |||
Latest revision as of 17:00, 16 October 2018
This section reviews a few of the basic building blocks for the other sections of the toolkit. Please contribute additional project management fundamentals or other examples to the DLF Project Managers Toolkit.
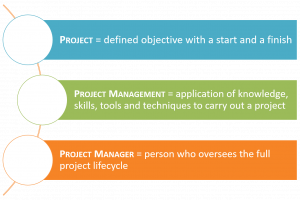
A PROJECT must have a defined objective (product, service, result) with a start and a finish. Projects should not be confused with ongoing work. For example, a digitization unit with regular requests for digitization is ongoing work, whereas a project would be to digitize a certain number of objects by a certain date.
PROJECT MANAGEMENT is the application of knowledge, skills, tools and techniques to carry out a project.
A PROJECT MANAGER oversees the project life cycle from planning, scheduling, executing, monitoring and controlling, and closing. There should only be one project manager in a project. Important characteristics for project managers are to be knowledgeable, performance-driven, and an effective communicator.
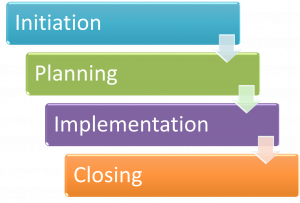
PROJECT PHASES include initiation, planning, implementation, and closing.
There are different factors or constraints to monitor and control in a project. Commonly known as the TRIPLE CONSTRAINT, the scope, time, and cost are managed and adjust in a project. Quality and risk should also be considered.
Project Management provides a framework and best practices for projects. For example, the following formula can be used to estimate the time of a task.
Three-Point Estimate
Determine: -optimistic value, D(o) -pessimistic value, D(p) -realistic value, D(r) Then: Duration = (D(o) + 4D(r) + D(p)) / 6
Critical to the success of any project is communication. Before beginning a project, consider the frequency (weekly, monthly, quarterly) and methods of communication (email, im, in-person; frequency of meeting). A communication plan should include the who, what, when, where, why & how. See the Project Templates of the DLF Project Managers Toolkit for an example of a communication plan.
References
- Project Management Institute. 2018. A guide to the project management body of knowledge: (PMBOK® guide). Newtown Square, Pennsylvania, USA: Project Management Institute.
- Tate, Karen, and Cynthia Snyder. 2006. The advanced project management memory jogger: a pocket guide for experienced project professionals. Salem, NH: GOAL/QPC.
There are lots of great articles, presentations and grey lit out there on project management and digital libraries. We've created a Zotero Group library at https://www.zotero.org/groups/2205688/dlf_pmg? and encourage you to add more when you read something good.

